Ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) is a synthetic rubber made up of ethylene and propylene with a small amount of a third monomer (usually a diene). Its molecular structure has a single bond, chemically saturated backbone, which makes it a polymer with excellent resistance to heat, weather and other demanding conditions. As the increasing demand of reducing the CO2 footprints, the ethylene propylene diene monomer from renewable ingredients has attracted more and more attention.
Synthesis of Bio-based Ethylene-Propylene Diene Monomer
Ethylene propylene diene monomer synthetic rubber was firstly created in the mid-1960s. As mentioned above, ethylene propylene diene monomer is a copolymer of ethylene, propylene and a small amount of non-conjugated diene monomers (3%-9%) which provide cross-linking sites for vulcanization (rubber hardening). The ‘bio-base’ in this material is attributed to the ethylene component of the ethylene propylene diene monomer. The ethylene content of ethylene propylene diene monomer rubber is around 45%-75%, and the higher the percentage, the more filler loading possibilities are presented.
Ethylene can be produced naturally by plants and some microbes that live with plants. And bio-based ethylene can supplement or replace fossil fuels as a base in chemical industry, using renewable sources of carbon such as waste biomass (plant matter). The general synthesis route is in figure 1 [1].
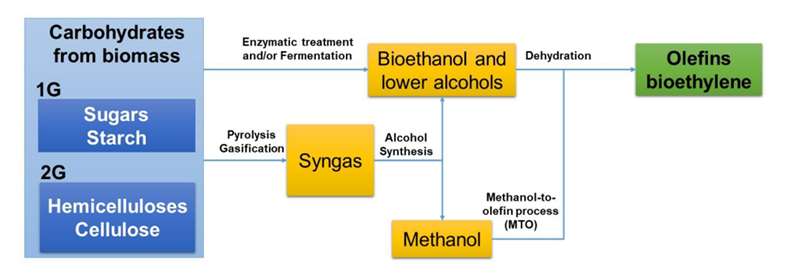 Fig. 1 The production process to make bio-based ethylene from carbohydrate biomass
Fig. 1 The production process to make bio-based ethylene from carbohydrate biomass
Applications
Due to its outstanding resistance to weather, ozone, and heat, as well as reduced dependence on fossil resources, and reduced carbon footprint. Bio-based ethylene propylene diene monomer can be used in many industries.

