Gastrojejunostomy (GJ) tube placement is a critical procedure designed to offer nutritional support to individuals who cannot consume or properly digest food through traditional means. This intervention is particularly useful for patients with severe gastrointestinal issues or conditions that prevent the normal function of the stomach. In this guide, we’ll delve into the details of GJ tube placement, including its indications, the procedure itself, benefits, potential complications, and care considerations. To get the best services of GJ tube placement click here https://www.appliedmedical.net/enteral/g-jet-family/.
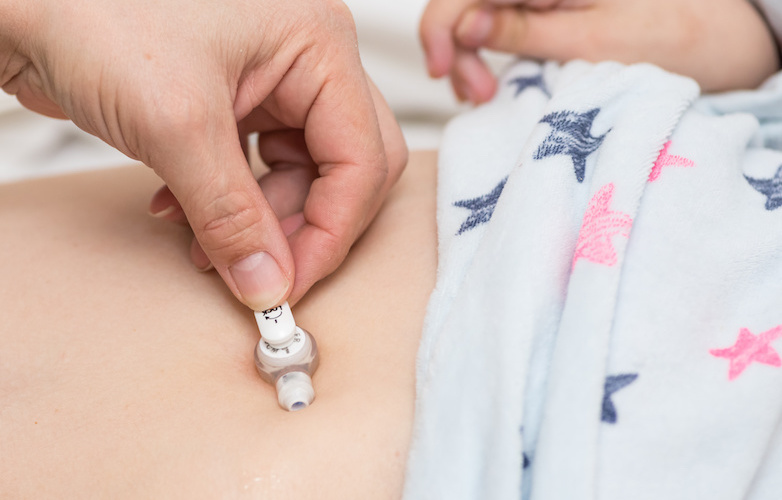
Image Source: Google
Understanding the GJ Tube
A GJ tube is a specialized feeding tube that extends from the abdominal wall into the jejunum, a section of the small intestine located beyond the stomach. This tube provides a direct route for delivering nutrients, bypassing the stomach entirely. The GJ tube is often chosen when a gastrostomy (G) tube, which delivers nutrition directly into the stomach, is not suitable due to issues such as impaired gastric emptying or severe gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
Indications for GJ Tube Placement
Several medical conditions may necessitate the use of a GJ tube:
- Severe Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): In patients with severe GERD, the risk of aspiration (where stomach contents enter the lungs) is high. A GJ tube reduces this risk by bypassing the stomach and delivering food directly to the jejunum.
- Delayed Gastric Emptying: Conditions such as gastroparesis or severe dysmotility can impair the stomach’s ability to process and empty food. In such cases, a GJ tube ensures that nutrients are still provided efficiently.
- Pancreatitis: Chronic pancreatitis can result in significant pain and digestive issues, making oral feeding difficult. A GJ tube can bypass the problematic area and help manage nutritional needs.
- Post-Surgical Complications: After certain gastrointestinal surgeries, such as those involving the stomach or duodenum, a GJ tube may be used to support nutritional intake while allowing healing.
The Procedure
You can also contact Applied Medical Technology if you are looking for the best gastric tube.The placement of a GJ tube typically involves several steps:
- Preparation: The procedure is performed in a hospital setting, often under sedation or general anesthesia. The patient is placed in a supine position, and the abdominal area is cleaned and sterilized.
- Initial Gastrostomy Tube Insertion: A gastrostomy tube (G tube) is first inserted into the stomach through a small incision in the abdominal wall. This tube acts as a guide for the placement of the GJ tube.
- Guidewire Placement: A guidewire is threaded through the G tube and advanced into the jejunum. This wire will serve as a pathway for the GJ tube.
- GJ Tube Insertion: Over the guidewire, the GJ tube is carefully advanced into the jejunum. Once correctly positioned, the G tube is removed, and the GJ tube is secured in place.
- Verification: The correct placement of the GJ tube is confirmed through imaging studies such as X-rays or fluoroscopy to ensure it is properly positioned in the jejunum.
- Post-Procedure Care: The insertion site is monitored for any signs of infection or complications, and initial feeding protocols are established.

Image Source: Google
Benefits of a GJ Tube
The GJ tube offers several significant advantages for patients with specific nutritional needs:
- Reduced Aspiration Risk: By bypassing the stomach, the GJ tube helps minimize the risk of aspiration, which can occur if food or liquids are inadvertently inhaled into the lungs.
- Effective Nutritional Delivery: For patients who cannot process food through the stomach, the GJ tube delivers nutrients directly to the jejunum, where absorption can still occur effectively. This ensures that essential nutrients and medications are provided efficiently.
- Improved Comfort and Quality of Life: Many patients experience relief from symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain when using a GJ tube, leading to a better overall quality of life.
- Flexibility in Feeding: The GJ tube allows for continuous or bolus feeding schedules, depending on the patient’s needs and preferences. This flexibility can be tailored to accommodate various nutritional requirements and lifestyle considerations.
Potential Complications
While the GJ tube can offer significant benefits, it is not without potential risks and complications:
- Infection: The insertion site is at risk for infection, which can be managed with proper hygiene and monitoring.
- Tube Displacement: The GJ tube may become dislodged or displaced, requiring repositioning or replacement. Regular checks are necessary to ensure the tube remains in the correct position.
- Blockage: The tube can become blocked by thickened feeds or medications, necessitating flushing and occasional maintenance.
- Leakage: Leakage around the insertion site or from the tube itself can occur, which may require medical attention to address and prevent complications.
- Abdominal Pain: Some patients may experience discomfort or pain around the insertion site or within the abdomen.
Care and Maintenance
Proper care and maintenance of the GJ tube are crucial for ensuring its effectiveness and minimizing complications:
- Regular Flushing: The GJ tube should be flushed with water before and after feedings and medications to prevent blockages and maintain patency.
- Monitoring the Insertion Site: The insertion site should be inspected daily for signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, or discharge. Keeping the area clean and dry is essential for preventing complications.
- Feeding Protocols: Following the prescribed feeding regimen, including the type and rate of feeds, is important for meeting nutritional needs and ensuring optimal tube function.
- Patient Education: Patients and caregivers should receive thorough education on how to care for the GJ tube, including how to handle feedings, recognize signs of complications, and perform routine maintenance.
- Regular Follow-Up: Regular follow-up appointments with healthcare providers are necessary to monitor the patient’s condition, adjust feeding protocols as needed, and address any issues related to the GJ tube.
Image Source: Google
Conclusion
GJ tube placement is a valuable medical intervention for individuals with severe gastrointestinal conditions that impair the normal process of digestion and nutrient absorption. By providing a direct route for nutrient delivery into the jejunum, the GJ tube helps improve nutritional intake, reduce the risk of aspiration, and enhance overall quality of life for patients facing challenging health conditions. While the procedure and its associated care require careful attention, the benefits can be substantial, offering critical support for patients in need.

